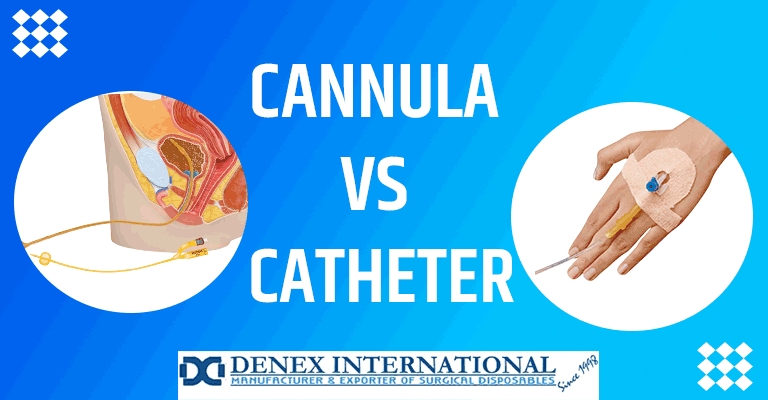
In the intricate landscape of medical devices, two terms often elicit questions and misconceptions: Cannula and Catheter. Navigating these essential instruments requires a keen understanding of their unique functionalities and applications. Denex International, at the forefront of healthcare solutions, invites you to delve into the complexities of Cannula vs. Catheter. This illuminating exploration sheds light on the distinctive features of these crucial medical tools. Join us in unraveling differences where precision meets clarity in medical instrumentation.
Understanding Cannulas:
Cannulas are essential medical devices designed to safely and precisely deliver fluids or extract substances from the body. These slender, tube-like instruments come in various sizes and configurations, each tailored to specific medical applications. Here’s a closer look at the critical aspects of understanding cannulas:

Intravenous Therapy:
Cannulas are commonly used in intravenous (IV) therapy to administer medications, fluids, or blood products directly into a patient’s bloodstream. They provide a secure and efficient way to deliver treatments without requiring repeated needle insertions.
Oxygen Delivery:
In respiratory care, cannulas are employed to deliver supplemental oxygen to patients. The flexible and lightweight design of oxygen cannulas allows for comfortable and continuous oxygen flow, making them suitable for short-term and long-term use.
Surgical Procedures:
During surgical interventions, cannulas serve various purposes. They can be used for the controlled delivery of anesthetic agents, the extraction of fluids, or as conduits for specialized instruments, contributing to the precision and efficiency of medical procedures.
Types of Cannulas:
Cannulas come in different types, including peripheral venous cannulas for routine IV therapy, nasal cannulas for oxygen delivery, and specialized cannulas for specific surgical applications. The selection of the appropriate cannula depends on the medical context and the patient’s needs.
Flexibility and Design:
Cannulas are known for their flexibility, allowing for easy insertion and maneuverability within the body. They are typically made from materials that are biocompatible and safe for medical use. The design may vary based on the intended application, with some cannulas featuring additional functionalities, such as ports for multiple infusions.
Short-Term Use:
While cannulas are generally suitable for short-term medical interventions, they are crucial in delivering immediate and therapeutic care. Healthcare professionals carefully select the size and type of cannula based on factors such as the patient’s age, medical condition, and the nature of the treatment.
Understanding cannulas is essential for healthcare professionals to ensure proper usage in various clinical settings. As integral components of modern medical care, cannulas contribute to the efficiency, safety, and comfort of patients undergoing multiple treatments and procedures.
Exploring Catheters:
Catheters are versatile medical devices introducing various body cavities, vessels, or ducts to perform specific functions. These flexible tubes find application in a wide range of medical procedures, aiding in the drainage of fluids, administration of medications, or facilitation of diagnostic interventions. Here’s a closer look at the critical aspects of exploring catheters:
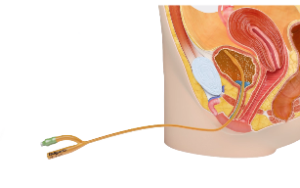
Urinary Catheters:
One of the most common applications of catheters is in urology, where urinary catheters drain urine from the bladder. Foley catheters, a specific type of urinary catheter, feature an inflatable balloon that anchors the catheter in place, allowing for continuous urine drainage.
Vascular Catheters:
Catheters are utilized in vascular procedures to gain access to blood vessels. Central venous catheters, for example, provide a route for administering medications, nutrition, or fluids directly into large veins. They are often used in critical care settings or for patients requiring long-term intravenous treatments.
Cardiac Catheters:
In cardiology, catheters play a vital role in diagnostic and interventional procedures. Cardiac catheterization involves the insertion of a catheter into the heart chambers or blood vessels to assess blood flow, measure pressures, or perform interventions such as angioplasty and stent placement.
Diagnostic Catheters:
Catheters are used for diagnostic purposes in various medical specialties. For instance, angiographic catheters are employed in imaging studies to visualize blood vessels and identify blockages or abnormalities. Similarly, catheters can be used to collect samples or perform procedures like endoscopy.
Flexible Design:
Catheters are characterized by their flexible and adaptable design, allowing them to navigate complex anatomical structures precisely. The flexibility of catheters is crucial for minimizing discomfort during insertion and ensuring accurate placement in the targeted area.
Short-Term and Long-Term Use:
The catheter may be utilized for short-term or long-term medical management, depending on the patient’s needs. Short-term catheters are often used for specific procedures, while long-term catheters may be necessary for patients with chronic medical conditions requiring ongoing support.
Exploring catheters involves understanding the diverse applications and variations within this category of medical devices. From urinary and vascular interventions to diagnostic procedures, catheters play a pivotal role in modern healthcare, contributing to the accuracy and effectiveness of medical treatments across different specialties.
Read Also: A Comprehensive Guide: IV Cannula Sizes,Colors, Flow Rates and Usage
Distinguishing Factors: Cannula vs Catheter
Functionality:
Cannula: Primarily used for administering or extracting fluids, such as in intravenous therapy or surgical procedures.
Catheter: Has a broader functionality, including draining fluids, administering medications, or facilitating diagnostic procedures in various body cavities or vessels.
Applications:
Cannula: Commonly applied in intravenous therapy, oxygen delivery, and specific surgical settings.
Catheter: Versatile, used in urinary catheterization, central venous access, cardiac procedures, and various diagnostic interventions.
Design:
Cannula: Typically smaller and more flexible tubes designed for specific applications.
Catheter: Designs vary based on the intended use, such as Foley catheters for urinary applications or specialized catheters for cardiac procedures.
Usage Duration:
Cannula: Often used for short-term treatments, providing immediate and precise delivery of fluids or medications.
Catheter: This can be employed for both short-term and long-term medical management, depending on the patient’s needs and the nature of the medical condition.
Flexibility:
Cannula: Known for flexibility, facilitating easy insertion and maneuverability within the body.
Catheter: Flexible design is crucial for navigating complex anatomical structures during various medical procedures.
Scope of Use:
Cannula: Specific to fluid-related applications, contributing to efficiency in intravenous therapy and surgical interventions.
Catheter: Wide-ranging applications addressing diverse medical needs such as drainage, medication administration, and diagnostic imaging.
Example Uses:
Cannula: Used for precisely delivering fluids, blood transfusions, or oxygen supply.
Catheter: Employed in urinary catheterization for drainage, central venous catheterization for intravenous access, and cardiac catheterization for diagnostic and interventional cardiology procedures.
Patient Comfort:
Cannula: Often chosen for its comfort during short-term use, particularly in intravenous therapy or oxygen delivery.
Catheter: May be used for both short-term and long-term applications, requiring careful consideration of patient comfort, especially in chronic medical conditions.
Understanding these distinguishing factors is crucial for healthcare professionals in selecting the most appropriate device for specific medical scenarios. Whether it’s the immediate precision of a cannula or the versatile functionality of a catheter, each plays a vital role in enhancing patient care across various medical specialties.
Place your order for IV cannula and Catheter in India at Denex International.
For those seeking reliable and high-quality IV cannulas and catheters in India, Denex International stands as a trusted source. With a commitment to excellence in healthcare solutions, Denex International offers a diverse range of IV cannulas and catheters designed to meet the varied needs of medical professionals. To place your order and ensure you have access to precision-engineered medical instruments, visit Denex International’s official website or contact their dedicated customer service. Experience the assurance of quality and efficiency as you procure IV cannulas and catheters from Denex International, a leading name in the healthcare industry.
Read Also: The Unseen Benefits of IV Cannula Without Wings and Port
Conclusion
In the realm of medical devices, precision is paramount. Understanding the distinctions between cannulas and catheters empowers healthcare professionals to make informed decisions, ensuring optimal patient care. Denex International, committed to advancing healthcare solutions, provides this informative guide to assist in navigating the nuances of these indispensable instruments. As you delve into medical devices, clarity on the differences between cannulas and catheters becomes valuable in delivering exceptional healthcare.