Even the most minor details can make a significant difference in patient care in medical advancements. One such piece that often goes unnoticed but plays a crucial role in the design of intravenous (IV) cannulas. This blog post will delve into The Unseen Benefits of IV Cannula Without Wings and Port, exploring their unique benefits and how they contribute to a more comfortable and efficient medical experience.
Understanding the Basics:
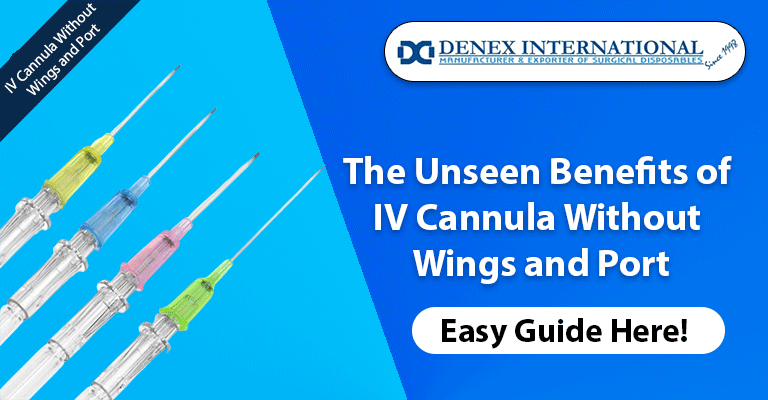
IV cannulas, commonly known as catheters, are thin tubes inserted into a patient’s vein to administer fluids, medication, or blood products. Traditionally, these devices come with wings and ports, but an emerging trend is gaining attention – the IV cannula without branches and ports.

The Unseen Benefits of IV Cannula Without Wings and Port
IV cannulas without wings and ports offer several profound benefits in medical settings, contributing to enhanced patient comfort, improved procedural efficiency, and minimized risks. Let’s delve deeper into these advantages:
Reduced Patient Discomfort:
The absence of wings eliminates the potential discomfort caused by traditional winged cannulas. Patients undergoing extended IV therapy experience less irritation and pressure on their skin, leading to an overall more comfortable experience.
Simplified Dressing Changes:
The wingless design facilitates dressing changes around the cannula site. Healthcare providers can efficiently perform these procedures without navigating around protruding wings, making the process smoother and more patient-friendly.
Minimized Infection Risks:
Cannulas without ports significantly decrease the risk of infection. With no additional entry points, the chances of pathogens entering the bloodstream are reduced, particularly crucial for patients with weakened immune systems or those undergoing prolonged IV therapy.
Streamlined Insertion Process:
The absence of a port simplifies the insertion process. Healthcare providers can establish vascular access more efficiently, saving time and minimizing patient discomfort during the procedure. This streamlined approach is particularly advantageous in emergencies.
Enhanced Pediatric Care:
Children, known for their sensitivity, benefit from the reduced discomfort provided by wingless cannulas. The absence of ports also decreases the likelihood of accidental dislodgment, making these devices especially suitable for pediatric patients.
Improved Emergency Response:
IV cannulas without wings and ports prove invaluable in emergency medicine, where time is critical. The quick and efficient insertion process aids healthcare providers in establishing vascular access promptly, ensuring timely administration of necessary medications or fluids.
Optimized Long-Term Therapy:
Wingless and portless cannulas offer an improved experience for patients requiring prolonged IV therapy. The reduced risk of complications and enhanced comfort during extended usage contribute to better patient compliance and outcomes.
Adaptability in Diverse Settings:
These innovative cannulas find utility in various healthcare settings, adapting to the specific needs of patients and providers. Their versatility makes them suitable for both routine care and specialized medical scenarios.
Conclusion:
Even the most minor innovations can profoundly impact patient well-being in the dynamic healthcare field. IV cannulas without wings and ports represent a subtle yet significant evolution in intravenous therapy. As healthcare providers continue to explore ways to enhance patient comfort and streamline procedures, these innovative designs are poised to become integral components of modern medical practices. In emergency settings or routine care, pursuing a more comfortable and efficient patient experience remains at the forefront of medical innovation.