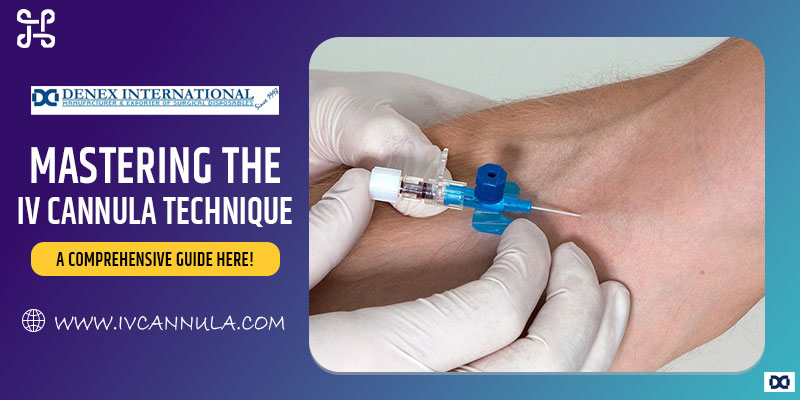
The intravenous (IV) cannula technique holds paramount importance in medical procedures. Whether administering fluids, medications, or blood products, mastering this technique is essential for healthcare professionals to ensure patient safety and comfort. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of the IV cannula technique, shedding light on its significance, steps, and best practices, including using a cannula fixator for enhanced stability and comfort.
Understanding the IV Cannula Technique:
An IV cannula, or an intravenous catheter, is a thin, flexible tube inserted into a patient’s vein to provide access to various medical treatments. The IV cannula technique involves precise steps to insert the cannula into the vein effectively while minimizing patient discomfort and the risk of complications.
Step-by-Step Guide to the IV Cannula Technique:
- Preparation: Before initiating the procedure, gather all necessary equipment, including the IV cannula, sterile gloves, antiseptic solution, adhesive dressing, securing device, and cannula fixator. Ensure proper hand hygiene and don personal protective equipment to maintain aseptic conditions.
- Patient Assessment: Assess the patient’s veins to determine the most suitable site for cannulation. Factors such as vein size, accessibility, and condition are crucial in site selection. Choose a visible, palpable vein that is free from any signs of inflammation or thrombosis.
- Vein Selection and Preparation: Once the ideal vein is identified, clean the surrounding area with an antiseptic solution and allow it to dry completely. Apply a tourniquet proximal to the intended insertion site to engorge the vein, facilitating cannulation.
- Cannula Insertion: Using an aseptic technique, stabilize the target vein and gently insert the IV cannula at a shallow angle (~15-30 degrees) with the bevel facing upward. Advance the cannula smoothly into the vein while maintaining a steady, controlled motion. As blood return confirms successful venous access, advance the cannula millimeters before retracting the needle.
- Needle Removal: Once the cannula is securely placed, retract the needle smoothly and discard it in a designated sharps container. Apply gentle pressure to the insertion site to minimize bleeding, and secure the cannula in place with an adhesive dressing and a cannula fixator for enhanced stability.
- Flush and Secure: Flush the IV cannula with saline solution to ensure patency and remove air bubbles. Secure the cannula and tubing using an appropriate securing device, ensuring the cannula fixator provides additional support and stability.
- Documentation and Monitoring: Document the procedure, including the site of cannulation, cannula size, and any pertinent observations. Regularly monitor the IV site for signs of complications, such as infiltration, phlebitis, or infection, and address any issues promptly.
Best Practices for IV Cannula Technique:
- Prioritize patient comfort and safety throughout the procedure.
- Maintain strict adherence to aseptic techniques to prevent infections.
- Choose the smallest suitable cannula size to minimize trauma to the vein.
- Opt for transparent dressings to facilitate visual inspection of the IV site.
- Rotate cannula insertion sites regularly to reduce the risk of vein damage or thrombosis.
Conclusion:
Mastering the IV cannula technique and using a cannula fixator for enhanced stability and comfort is essential for proficient patient care in healthcare settings. By following proper protocols, employing meticulous techniques, and prioritizing patient well-being, healthcare professionals can ensure successful venous access and optimal treatment outcomes.
Denex International, a trusted manufacturer of high-quality IV cannula products and cannula fixators, committed to advancing patient care through innovation and excellence in medical devices.